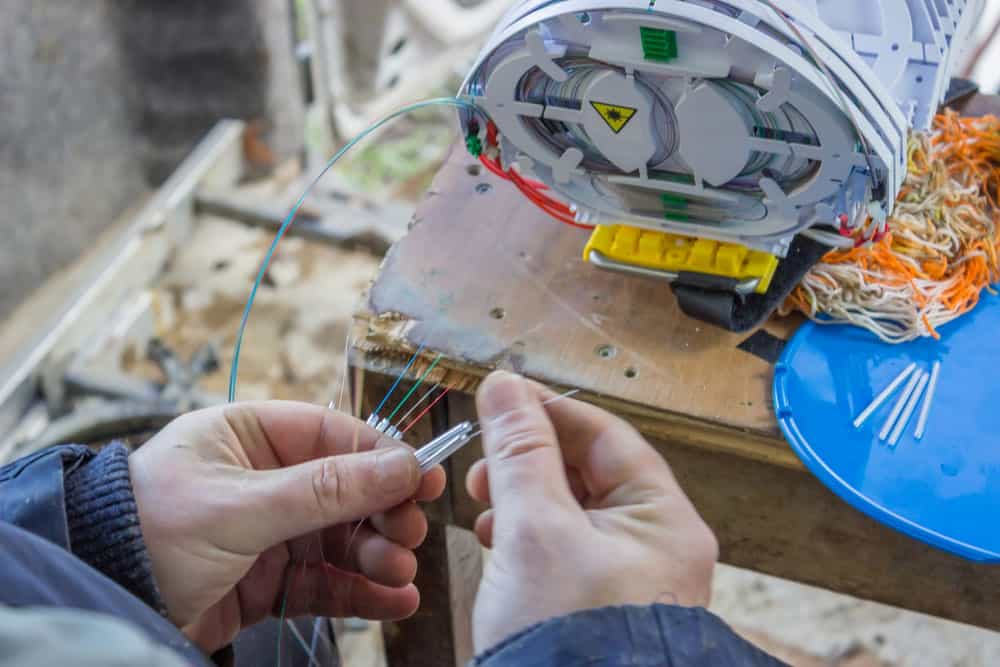
If you pride yourself on exploring your car’s mechanism, you’re probably aware of the vehicle’s wiring. However, if you’re new, this could be a challenging experience and you are supposed to begin with the term, automotive wiring harness wire.
What Is Automotive Wire?
Put it in simple terms; an automotive wire is simply a wire that’s best suited for automotive wire harness purposes.
Different types of automotive wires or cables are designed to serve specific purposes. The most common wires you’re likely to come across are the brake, speaker, primary, and battery cable.
If you pick the wrong type of wire for a specific application, it will lead to system failures in your car. Furthermore, improper Wiring could result in an engine fire.
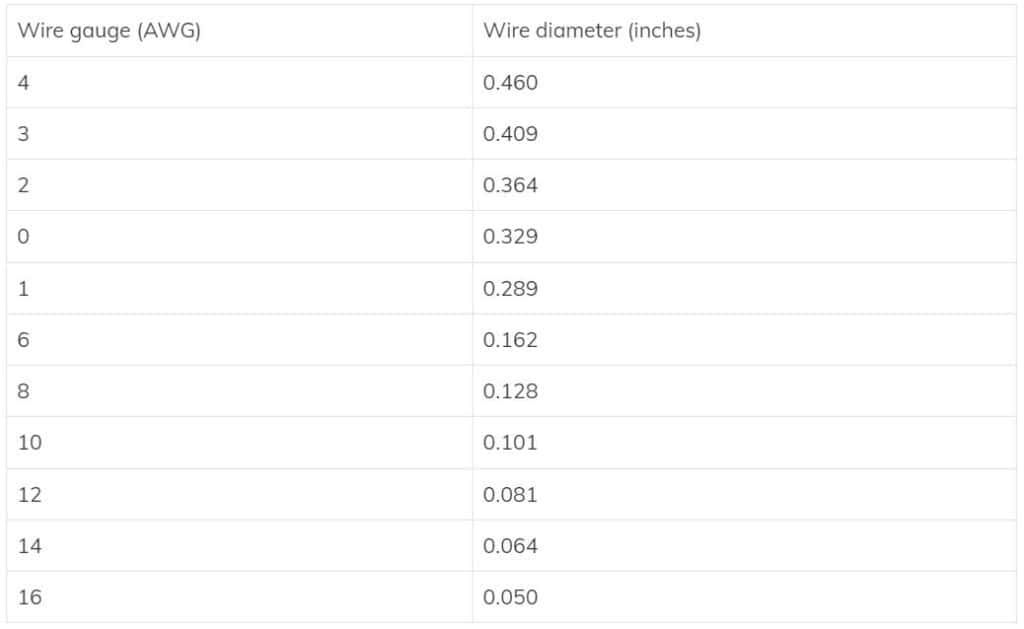
Also, as a side note, a wire thicker than gauge 8 is referred to as a cable.

Engine fire
Different Types of Automotive Wires and Cables
The following are different wires used in vehicles.
GPT or Primary Wire or Main Wire
This wire is probably the most common one you’ll come across in any vehicle’s wiring system. The primary wire (GPT) has a multi-strand core with flexible insulation to allow it to fit through tight spaces. They’re mainly used for interior wiring purposes. They’re used primarily for internal wiring purposes. GPT wires should not be exposed to the outdoors for prolonged periods.
Primary wires can endure temperatures of up to 176 Fahrenheit. They can also withstand chemicals, acids, and oils without complications.
Motor Wire
The motor and main wires differ because the motor wire’s insulation has more delicate strands of copper. They usually can withstand up to 600 volts and temperatures as high as 2210F. Also, it can withstand higher voltages without any complications.
TXL, GXL, SXL Wire
Wires made of single-stranded conductor type of copper are usually TXL. These wires have cross-linked polythene to insulate them. GXL wire is a single-conductor primary wire with XLPE insulation. SXL wire, on the other hand, has a bare copper conductor and is protected with XLPE.
The jacket made of cross-linked polyethylene means the wires have better aging, abrasion, and heat resistance.
Further, depending on the application area, the insulation thickness differs. The TXL wire differs from the other two types because it has thinner insulation. And GXL wires are a cross between SXL and TXL wires in terms of thickness.
Due to its extra durability, the SXL wire is preferred for more intense conditions such as industrial or racing vehicles. However, TXL wires are also used in racing vehicles because they are lighter, helping save on weight.
Battery Cable
The battery harness cable connects the battery to the ground and the electrical system. Often it’s thicker in size than most wires.
Speaker Wire
You’ll need speaker wires to transmit audio signals from the stereo receiver to the speakers. Typically, speaker wires serve low voltage purposes. To ensure the speaker sounds right, properly connect the negative and positive terminals of the wire.
Trailer Wire
It refers to the primary wire that’s been tailored and colored to serve as a trailer wire. Often trailer wires utilize a color code of brown, green, white, and yellow.
Colorful wires
Difference Between a House Wire and Automotive Wire
Automotive wires are often used in harsh environments of your vehicle. For instance, they’re used in the engine where if house wires were in the application, they could easily get damaged upon coming into contact with battery acid.
In contrast, automotive wires can withstand high temperatures and chemical corrosion. Also, automotive Wiring is a more robust and secure jacket while maintaining more flexibility than house wires.
A common mistake many people make is opting for house wires to serve automotive purposes simply because they’re cheaper. Even if the housing wire you picked fits the ideal current carrying capacity, several other factors remain to consider.
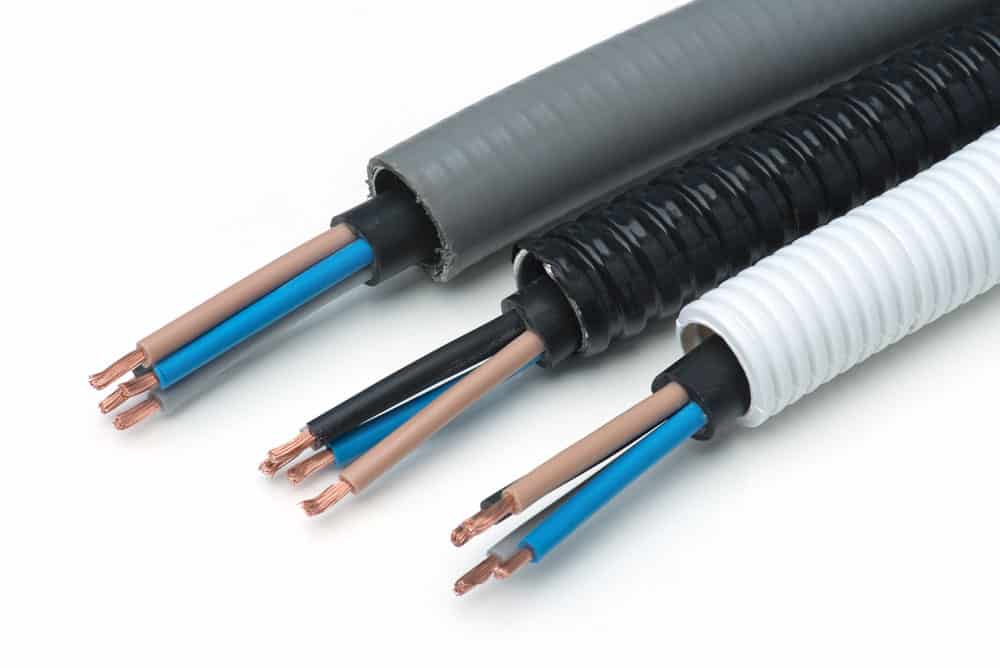

Wire conduits
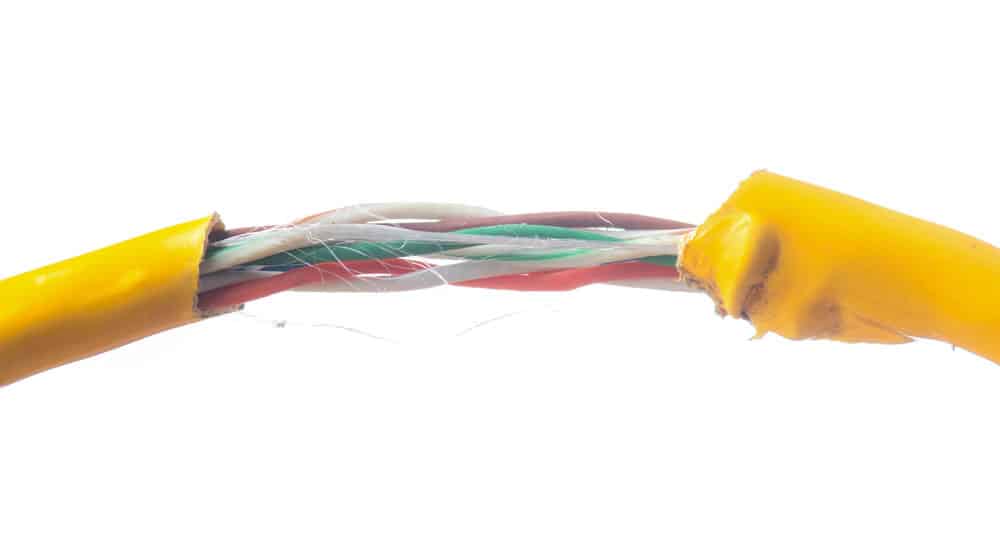
Common Vehicle Wire Damages
Due to some reasons, your automotive Wiring suffers a lot from:
Short Circuit
If the Wiring to the ground or electrical power source is short, it will cause some components in the circuit to malfunction or perform partially. However, it depends on where the Wiring is lacking and how fast it is.
Open Circuit
If any wire in your system is cut, no current can move from one end of the circuit to the other. Such instances result in an open course.
High Resistance
High resistance can block the current flow, resulting in some of the circuit’s electrical components malfunctioning. The High resistance is often caused by improperly connected Wiring or rusted wires and components.

Interior wiring
What Are the Signs Your Car Has Damaged Wiring?
Wires have conduits that allow the safe passage of electricity along various circuit parts. In case of a wire malfunction, your vehicle will display some signs in correspondence to the connected electrical device.
Malfunctioning of Vehicle Electrical Components
Faulty Wiring could result in several electrical issues, such as a broken radio or lights.
Fuse Keeps Blowing
A fuse is designed to blow if excess volts of electricity pass through a given circuit. If your vehicle has a shorted wire, it could result in excess electricity flowing through a course, which will trigger the fuse to blow.
Car Won’t Start
It’s common for your vehicle to exhibit some issues starting if there are any wiring issues. The problems range from PCM ground wire corroded to a damaged wire in the starting circuit.

How to Choose Vehicle Wires
When picking a wire for your project, some factors should help you make the best decision.
Wire Size
Wires are measured according to their gauge size. However, the gauge scale is inverted, with the thicker wires having a smaller gauge size. For instance, a 10-gauge wire is more comprehensive than a 20-gauge one.
The amount of current drawn from the circuit and wire length between the electric power source and the course will guide you in picking the correct gauge size to serve your needs better and ensure complete Wiring.
However, if your intended use is doing repairs, ensure you have the technical manuals for vehicles to avoid making costly mistakes. The manual will help guide you as it will likely always have the exact gauge size required for specific automotive components.
Wire Amperage
Amps determine the total amount of electricity a wire can allow to flow through.
Before purchasing any electrical wires, carefully check the label to determine the current rating. Overloading a wire is dangerous and could lead to shorting out, damage to essential systems, stalling equipment, or in some extreme cases, it could spark a fire. It’s advisable always to ensure you have the right amp rating before buying any wires.
Ensure you know the relays, circuits, breakers, fuses, and any other form of overload protection your wiring project needs. In addition, have suitable automotive wiring connectors for the job. Excess amps will likely short out your connectors.
Wire Materials: Copper or Aluminum
Electrical cables and automotive wire materials are mainly available in two forms; aluminum and copper. Copper wires are often the right choice for automotive wire harness applications. Copper wires are more flexible and conductive compared to aluminum. Also, copper wires are less likely to corrode.
Aluminum wires, on the other hand, are considered lighter and cheaper. However, they are less durable and more susceptible to corrosion. Also, over time, aluminum wires are likely to develop electrical resistance.
Wire Core: Stranded or Solid
Solid wire is mainly suitable for the wiring harness industry and home use. It’s best to avoid using reliable cables in your car’s Wiring unless you plan on using them to bail wires. With automotive Wiring, you should opt for flexible Wiring. Stranded wire is more flexible since solid core wires can’t bend over and over.
Insulation: Cross-Linked or PVC.
To create PVC insulation, first, heat the PVC. Then there’s a die on the stranding through which the PVC is extruded. The insulation is then added via melting through a heat source, which could change the form. There are three main categories of PVC automotive wires:
GPT: Rated 80 °C and suitable for common types of circuit wiring.
HDT: Also rated 80 °C and used as automotive wire for heavy walls.
TWP: Rated 105 °C and used primarily as a thin wall automotive wire. It’s also considered lead-free.
To create cross-linked insulation, first, you’ll use a tube to extrude the polyethylene while keeping it under high pressure and heat. This will cross-link the molecules to another state. Compared to PVC automotive wires, automotive cross-link wires can withstand far higher temperatures, better serving the wiring harness industry. The three most widely used cross-linked automotive cables include:
GXL: Rated 125 °C, considered thin wall, and suitable to work with typical automotive types of connectors.
SXL: Rated 125 °C and considered a standard wall.
TXL: Also rated 125 °C, considered fragile wall and best suited for application on wire harnesses requiring small size and minimal weight.
Wire Coloring, Striping, and Printing
Automotive wires are available in a variety of colors. A more straightforward way to organize the necessary cables to accomplish a task or repair is to assign colors to the wires according to the intended use.
You can use colors to identify and track wires back to their circuit. Today, various market sectors have their standard wire color system. Furthermore, you can expand the color scheme by adding a color stripe.
You could purchase wires with printed wording indicating their exact use for further clarity. Quickly sorting your wires allows you to conduct repairs and efficient constructions efficiently. You’ll develop a color code for future custom wire stripping tasks, saving time.
Connections
Generally, Wiring uses two types of automotive wire connections; solderless and soldered.
Often, solderless connections are considered the quickest and easiest way to terminate wires. Solderless bonds involve readily available automotive wiring connections such as ring terminals, spade terminals, and quick disconnects.
To properly use the following equipment, it’s advisable to learn how to make a proper crimp. Unfortunately, solderless connections aren’t always as long-lasting as the ones you’d wish. However, you could use additional strain relief equipment, such as auto wiring harness tape or heat shrink tubing, to increase the lifespan of solderless connections.
On the other hand, soldered connections are more susceptible to error and difficult to install. With the wide variety of solderless links to pick from, it’s rare to find people using soldered connections. Many professionals today discourage soldered associations because it makes it harder to control quality during the process.
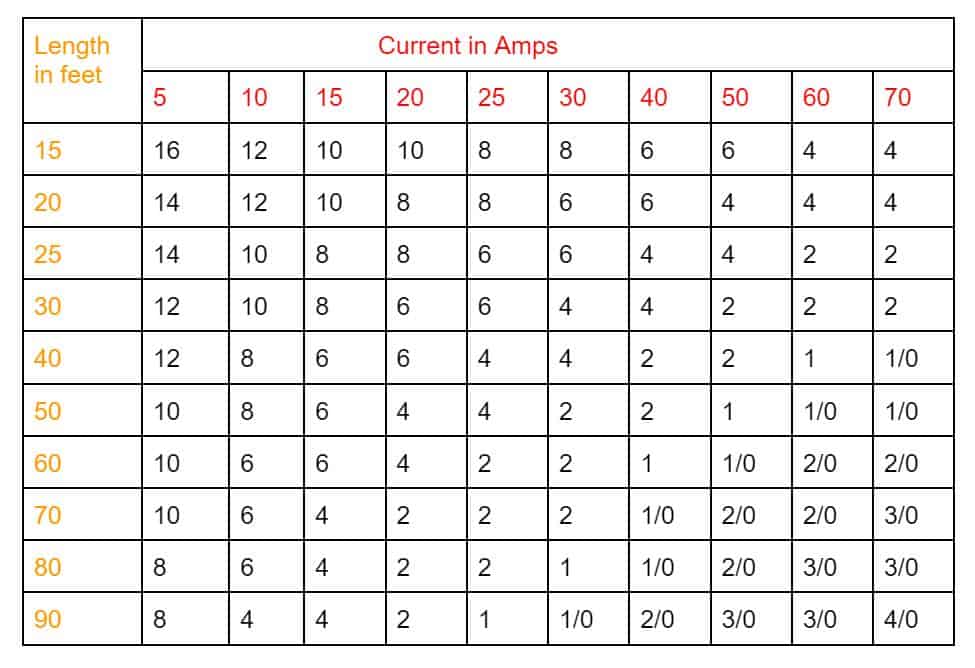
Wire Length
Wire length chart by amps and wire gauge.
Conclusion
There are different types of automotive wiring harness wires, each with other properties. Wiringo is one of the leading wiring harness wire manufacturers, serving automotive companies. Any signs of wiring damage? Look to us for help.