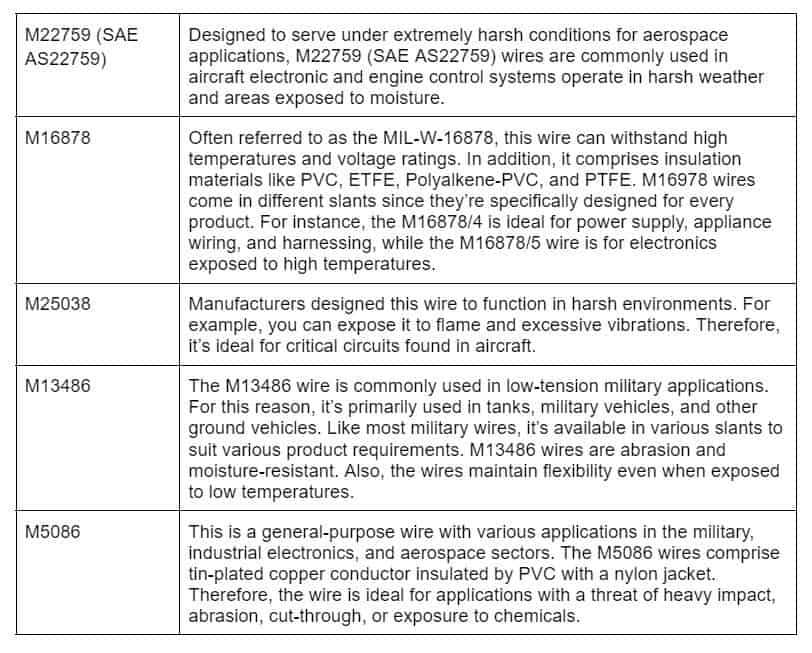
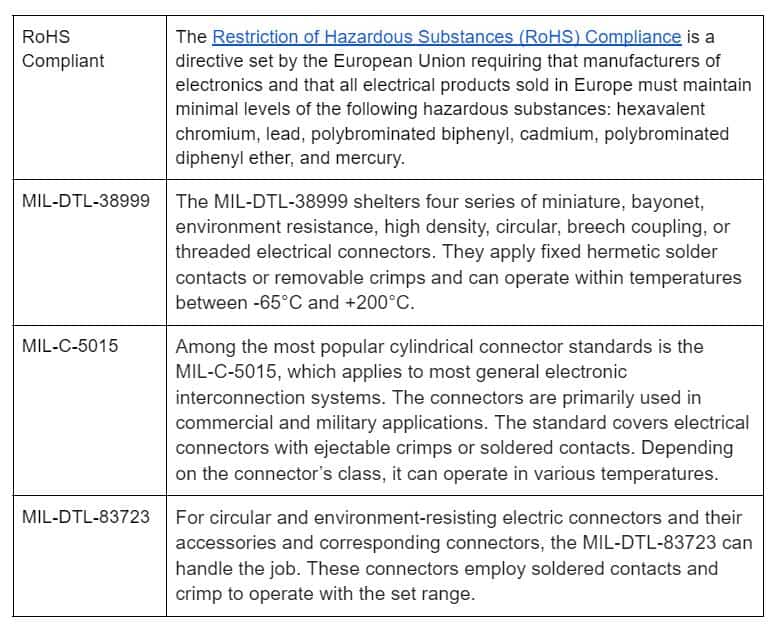
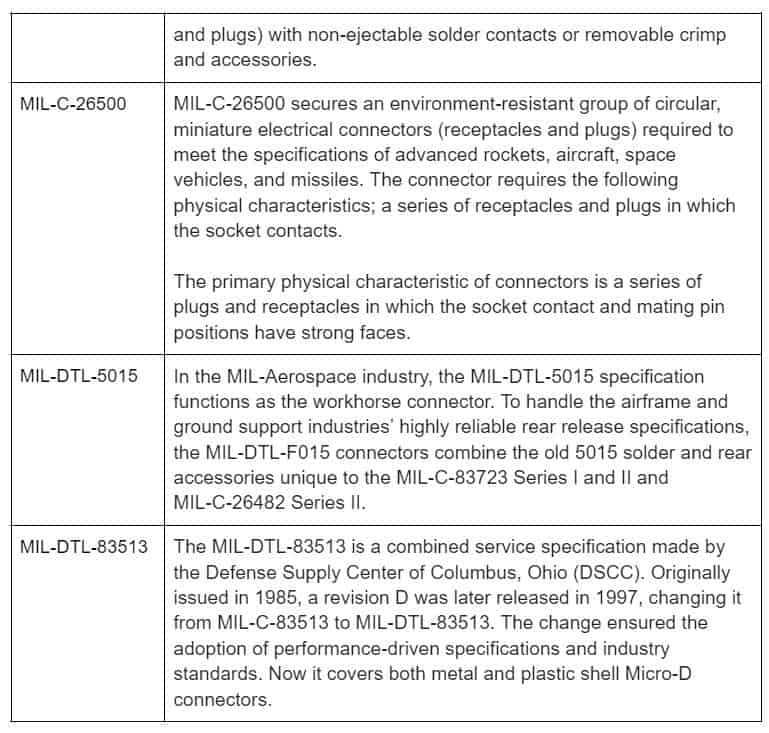
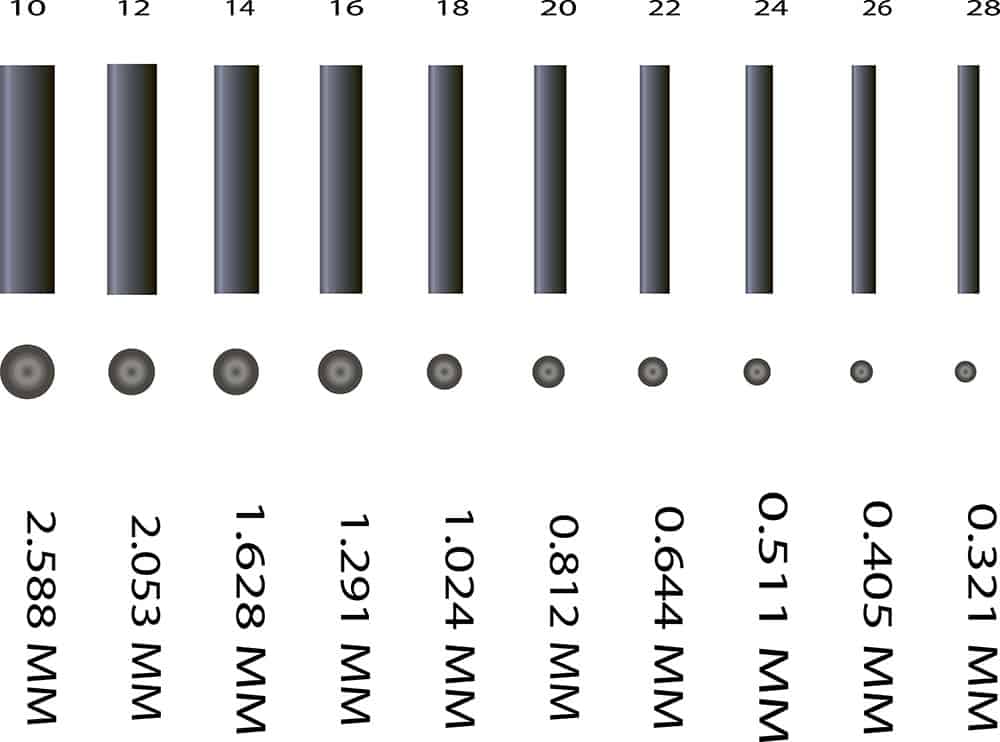
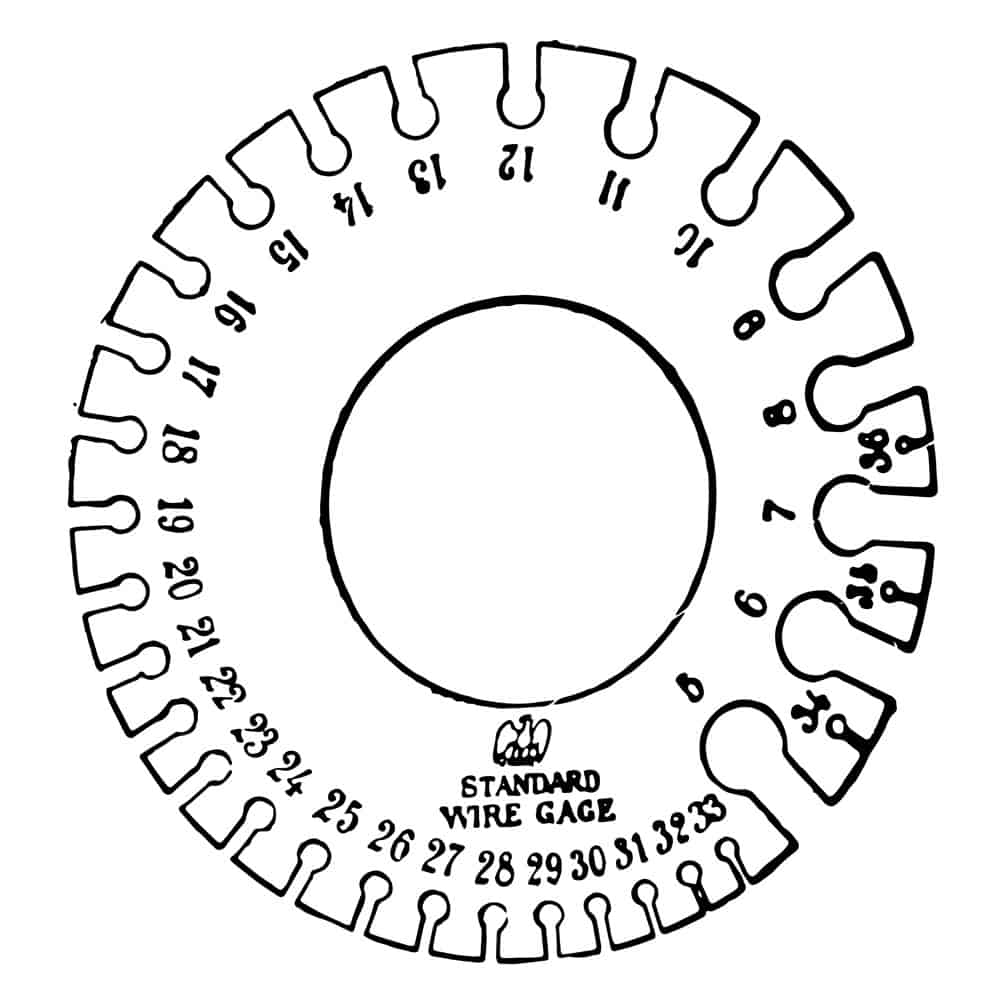
Automation in the house and factory relies on the gadgets’ communication abilities. People expect that industrial equipment should communicate with one another as technologies evolve.
D-sub connectors were the standard for making connections before twisted-pair connections became commonplace in factories. Furthermore, D-sub connectors have been around since the ’50s and still are a popular choice for today’s equipment. Let’s check out the D-sub cable assembly explicitly built for this project.
What are D-sub cables?
D is for “D” shape connectors. As an acronym for “sub-miniature,” “sub” means something smaller than a standard miniature. It’s a multi-wire cable with “D”-shaped plugs at each end.
There are different “standard density” pin counts for sub-connectors, such as 9, 15, 25, 37, and 50. Also, these cables can have high-current connection pins and coax connector pins, which adds an extra layer of complexity. There are component engineers whose sole job is to keep track of all the permutations of configurations.
VGA cables are the most common type of D-Sub cable that you can find in homes with a standard density of 15-pin. Moreover, you may find it in machinery for operating a “lift chair” with an average thickness of 9-pin.
These cables usually use multi-conductor wire with a grounding shield. The protection prevents interference from getting into your electronics by blocking RF sounds and signals.
Among the many possible industrial applications is the transmission of control signals during the production process, Electronic testing, and the interconnection of various components of CNC routers, Press Brakes, etc. Some could even be in your automobile.

Caption: Computer Monitor Port
Typical applications of D-sub cable assemblies
Here are some common examples & applications for D-Sub Cables
Communications ports
You can find D-sub connectors in RS-232 serial transmission, but this is not because they meet any standards. Although DB25 was a popular choice for these devices, signal degradation forced people to switch to DE-9 Connectors.
The IBM PC, for instance, employs both the male and female connectors found on the modem. You can also find DE-9 in the serial interface on Apple Macintosh computers.
Network ports
When manufacturers first introduced the DE-9 adapters, they used a combination of Token Ring and other network technologies.
In the 1980s, electricians utilized a DA15 connector for connectivity on attachment unit interfaces. The sliding latch was far more dependable in these systems than the jackscrew.
Computer video output
The IBM PC’s visual output was a female 9-pin connector. In theory, you could connect different kinds of outputs to the same connector, but this could hurt the interface.
Therefore, the VGA cables with their DE15 high-density connections were visible much later. Manufacturers also included the “D-Sub 15-pin” connector sockets for RGB video output on many Apple Macintosh models.
Game controller ports
The industry used the DE9 connector on the first Atari gamepad. As they made it out of plastic, it lacked the jackscrews required to secure it in the socket. The connector used by the game ports eventually became standard across various gaming consoles.
Others
There were external floppy drives in the original Macintosh and the Apple II that came after it. D-sub connectors make it possible to connect hard drives and printers, and both Apple and Atari’s 16-bit computer lines have them.
In addition, several manufacturers have integrated D-sub connections into their video and audio transmitters.

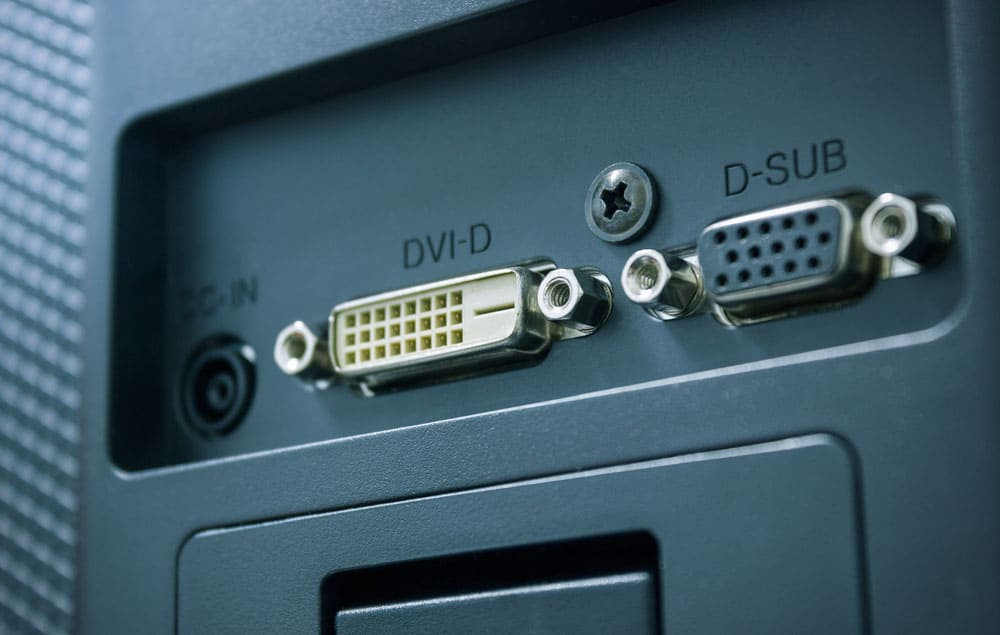
Caption: Ports on Video card
Wire-contact attachment types
D-sub connectors help attach wires and come in six different varieties.
- Insulation Displacement contacts: Ribbon cables are inserted into pointed tines on the contacts’ reverse side with insulation displacement contacts. That allows you to penetrate the shielding of all the wires simultaneously. Whether you do it manually or using a machine, it doesn’t take long.
- Solder Bucket: The stripped wire is placed into the cavity of the soldering tool before being hand-soldered.
- Wire-Wrapped Connections: Solid wire-wrapped connections are wrapped around the square post using a wire-wrapping tool. That is a valuable type to have on hand while creating prototypes.
- Crimp Contacts: Wires are inserted into the crimp contact’s cavity in the back, which is then compressed using a crimping tool. That allows the cavity to grab the wire in multiple locations effectively. The crimped contact is then inserted into the connector and then removed with the use of dedicated equipment and methods.
- PCB pins: PCB pins are soldered into the board without wires. Initially, THP board-style connectors were standard, but these proved problematic when they faced mechanical force. That explains why PCB connectors became standard in electronics.

Caption: D-Sub miniature port on the motherboard
Advantages & Benefits of D-Sub Connectors
Some users may not understand why D-Sub connections are still in the market when more advanced options exist. Compared to USB, USB-C, and MDP connectors, D-Sub connectors have a variety of benefits.
- Secure Connection: D-Sub connections are popular because of their lock-down feature, which ensures that the link remains safe even after being subjected to vibration and jostling.
- Design Flexibility: Standard D-Sub wire assemblies can have anything from 9 pins to 50 pins, and high-density variants can increase that to 78 pins, albeit most users are only familiar with the nine-pin and 15-pin connectors. Additionally, they provide simpler connection rewiring, reconfiguration, and fine-tuning.
- Cost Efficient: D-Sub cables are more affordable than other types of connections because of the low cost of the components and the ease with which they may be assembled.
- Large Variety: D-Sub cable assemblies can be either through-hole or surface-mounted on a printed circuit board, can be stacked, and feature EMI/RFI filtering for extremely noisy settings. Solder joints, crimping, insulation displacing, wire-wrap, and mass terminating are all viable alternatives for securing the ends of D-Sub cables. With combination connectors, you may get an even reduction in the number of signaling contacts required for coaxial, high current, or high voltage links.
- Multiple Uses: D-Sub connectors are the greatest option for many media applications in televisions, video games, and recording equipment because of their low cost and reliability.
- Longer lasting: D-Sub cables are built to last, making them ideal for mobile use where frequent reconnection and bumping are potential wear and tear issues.
Custom D-sub cable assemblies at Wiringo
Custom D-Sub connectors can help fit the needs of any design, even in extreme conditions. These cable connections can function as input/output connections. They can pair with a printed circuit board (PCB) or wire connectors. Crimps and solder buckets are an option. Using hoods and lock systems, you can avoid accidental un-mating and lifting.
Here are a few options we offer you
- Standard and industrial D-Sub connections with a single or double end.
- Termination of various Custom Serial Cables, such as D-SUB, DB9, DB15, DB37, DB25, HD50, etc.
- Unshielded and Shielded Wires
- Heat-shrink and bespoke labels
- Shielding, jacketing, inner/outer molding, contact electroplating, and bolt types.
- Cables with a D-Sub Hybrid Connector
- D-Sub and Backshell Cans of Military Quality
- Cable LSZH
- Reconfigurable Pins
- Logos and Specialized Castings
Roduct display
- R/A DB9 Female to Multi-Legged Coax Cables
- DB9 Female to RJ45 Cable
- DB9 Military Grade Cans to Mil-C D38999 with RJ45
- DB15 Male to Female with Coax Leads Custom Cable
- DB25 *4 Female Panelmount on Internal SCSI Ribbon Cable
- D-Sub 25 w/ Ferrite
- DB25 Male/Male or Female Cables – Fully Populated, Double Shielded, Black/White
- DB37 Male/Male or Female Cables – Fully Populated, Double Shielded, Black/White
- DB15 Male/Male or Female Cables – Fully Populated, Double Shielded, Black/White
- DB9Male/Male or Female Cables – Fully Populated, Double Shielded, Black/White
- HD15 Male/Male or Female Cables – Fully Populated, Double Shielded, Black/White
- Dual DB15 Female Panelmount with IDC Sockets on Ribbon Cable
- D-Sub 9 to 3.5mm Stereo Plug
- DB25 Male/Male or Female Cables – Fully Populated, Double Shielded, Black/White
- DB37 Male/Male or Female Cables – Fully Populated, Double Shielded, Black/White
- DB15 Male/Male or Female Cables – Fully Populated, Double Shielded, Black/White
- DB9Male/Male or Female Cables – Fully Populated, Double Shielded, Black/White
- HD15 Male/Male or Female Cables – Fully Populated, Double Shielded, Black/White
Conclusion
Most of these gadgets’ connection points are D-sub connectors. They make connecting them to a network or transmitting audio/video signals easy. You can customize these ports and make them robust, flexible, and secure. Here at Wiringo, we offer wiring harness solutions and custom cable assemblies to make your connection safe and reliable.